A new study shows that one in three patients with a severe skin disease were able to regrow hair after being treated with a common arthritis drug.
The study is based on Phase 3 clinical trials using baricitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, to treat alopecia areata, an often disfiguring skin disease characterized by rapid loss of scalp hair, and sometimes eyebrows and eyelashes.
Phase 3 clinical trials are the final testing hurdle before a new treatment can be considered for U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval. There is currently no FDA-approved treatment for the disease.
Dr. Brett King, an associate professor of dermatology at the Yale School of Medicine and lead author of the new study, published March 26 in the New England Journal of Medicine, said:
This is so exciting, because the data clearly show how effective baricitinib is. These large, controlled trials tell us that we can alleviate some of the suffering from this awful disease.
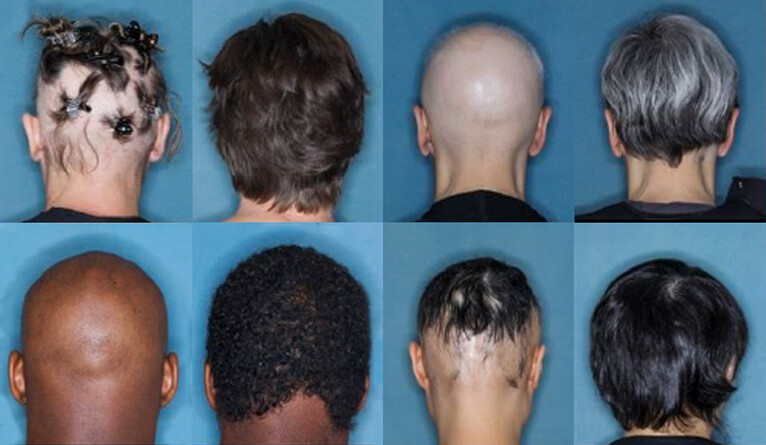
For the new study, King and his colleagues conducted two large, randomized trials involving a total of 1,200 people. The participants were adults with severe alopecia areata, who had lost at least half of their scalp hair; many had lost all of their scalp hair.
For 36 weeks, participants were given a daily dose of either 4 milligrams of baricitinib, 2 milligrams of baricitinib, or a placebo. One-third of the patients who received the larger dose grew hair back.
The researchers said baricitinib thwarts the disease by disrupting the communication of immune cells involved in harming hair follicles. Baricitinib and other JAK inhibitors are routinely used to treat autoimmune forms of joint disease.
Co-authors of the study included researchers from the Kyorin University Faculty of Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Stanford University, the University of California-Irvine, the University of Minnesota, Eli Lilly and Company, and Sinclair Dermatology.
The results of the study were made public during the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. For the past decade, King has developed methods for using JAK inhibitors to treat a variety of skin diseases — including eczema, vitiligo, granuloma annulare, sarcoidosis, and erosive lichen planus.
Dr. Brett King is also a consultant to and a clinical trials investigator for Eli Lilly and Company, witch funded the research.
King noted that the clinical trials involving baricitinib are ongoing, which will enable researchers to assess the long-term effectiveness and safety of the treatment.
